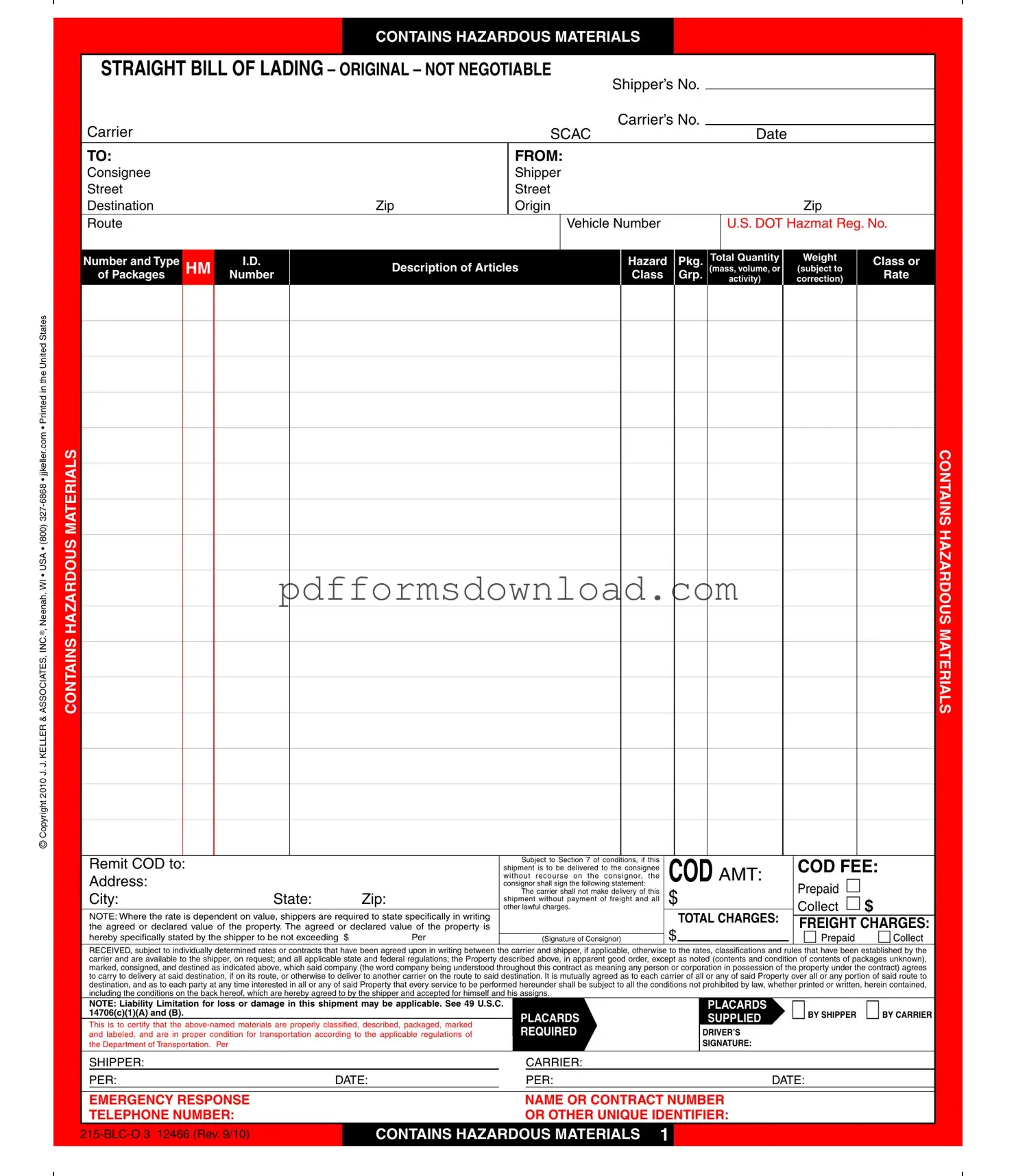
What is the Hazard Bill of Lading form?
The Hazard Bill of Lading form is a document used in the transportation of hazardous materials. It serves as a receipt for the goods being shipped and outlines the terms and conditions under which the carrier agrees to transport these materials. This form is crucial for ensuring compliance with federal regulations and for providing necessary information about the nature of the goods being transported.
Why is the Hazard Bill of Lading important?
This form is essential because it helps ensure the safe and legal transportation of hazardous materials. It provides detailed information about the contents, including their classification, weight, and any specific handling requirements. Additionally, it protects both the shipper and the carrier by clearly outlining their responsibilities and liabilities in the event of loss or damage during transit.
Who is responsible for filling out the Hazard Bill of Lading?
The shipper is primarily responsible for completing the Hazard Bill of Lading. This includes providing accurate descriptions of the hazardous materials, including their classification and any special handling instructions. It is vital that the shipper ensures all information is correct to avoid potential legal issues or delays in transportation.
What information must be included on the Hazard Bill of Lading?
Key information required on the Hazard Bill of Lading includes the shipper's and consignee's details, a description of the hazardous materials, their classification, weight, and any specific handling instructions. Additionally, the form must include payment terms, liability limitations, and signatures from both the shipper and the carrier. This comprehensive information helps facilitate safe transport and compliance with regulations.
What happens if the Hazard Bill of Lading is not filled out correctly?
If the Hazard Bill of Lading is not completed accurately, it can lead to serious consequences. Incorrect information may result in delays, fines, or even the refusal of the shipment by the carrier. In some cases, it could expose the shipper to liability for any accidents or incidents that occur during transportation. Therefore, attention to detail is crucial when filling out this form.
What are the liability limitations outlined in the Hazard Bill of Lading?
The Hazard Bill of Lading includes specific limitations on liability for the carrier. Generally, the carrier is only liable for the lesser of the actual damages or the declared value of the property. This means that if the shipper has not declared a value for the goods, or if the declared value is less than the actual damages, the shipper may not be fully compensated for losses incurred during transit.
How long do I have to file a claim for loss or damage?
If there is a loss or damage to the property, claims must be filed in writing with the carrier within nine months of delivery. In cases where delivery has not occurred, claims should be filed within nine months after a reasonable time for delivery has elapsed. Failing to file a claim within this timeframe may result in the loss of the right to seek compensation.
What should I do if the hazardous materials are refused at delivery?
If the hazardous materials are refused at delivery, the carrier may sell the goods at public auction after notifying the shipper. However, the carrier will first attempt to contact the shipper for instructions on how to proceed. If the materials are perishable, the carrier has the right to sell them quickly to prevent further deterioration. It's important for shippers to stay informed and responsive to avoid complications.