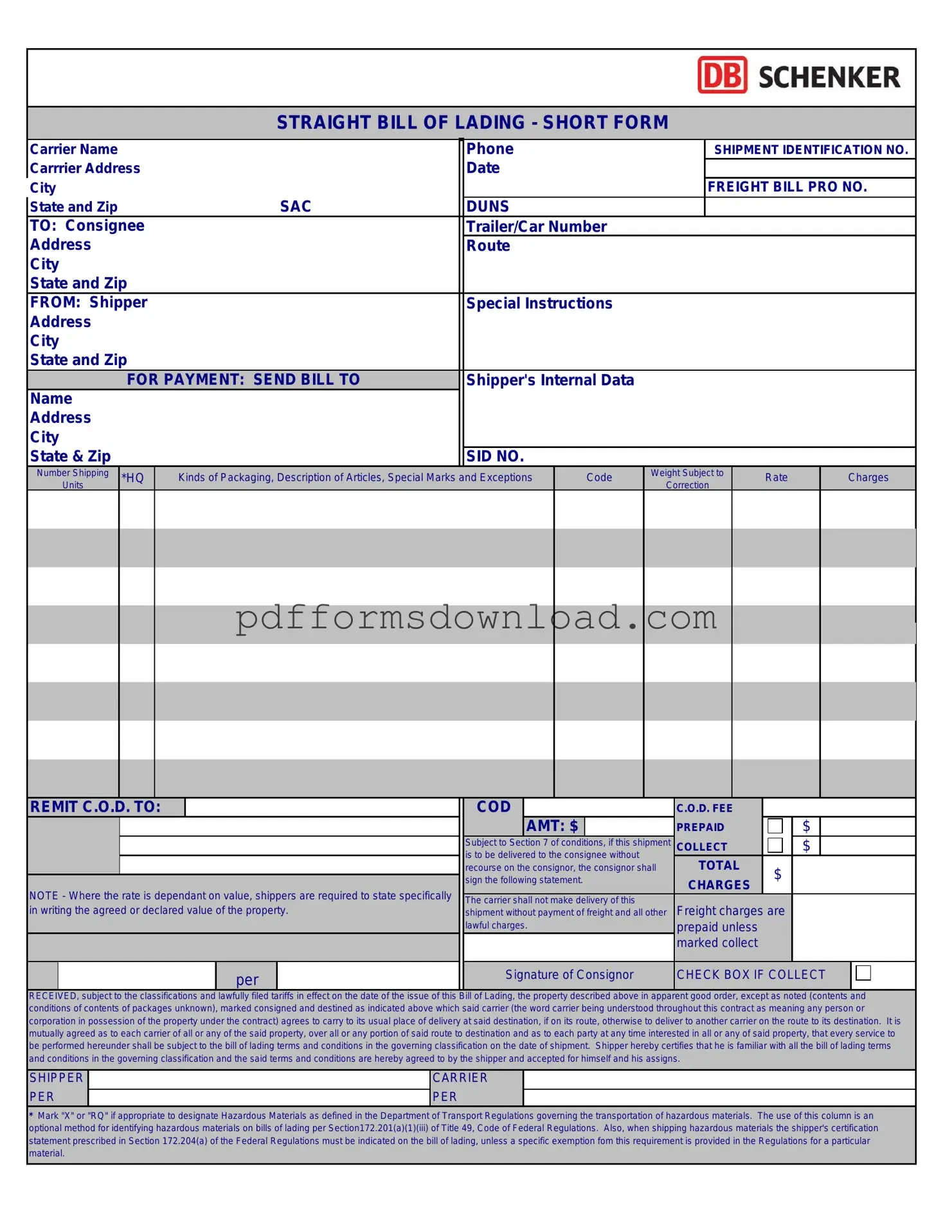
What is a Straight Bill of Lading?
A Straight Bill of Lading is a shipping document that serves as a receipt for goods and a contract between the shipper and the carrier. It indicates that the goods are being transported to a specific consignee and cannot be transferred to another party. This type of bill of lading is typically used when the shipper wants to ensure that the goods are delivered directly to a designated recipient without the option for negotiation or transfer of ownership during transit.
What information is included in a Straight Bill of Lading?
The Straight Bill of Lading includes essential details such as the names and addresses of the shipper and consignee, a description of the goods being transported, the shipping route, and the terms of the shipment. It may also contain tracking numbers, weight, dimensions, and any special handling instructions. This comprehensive information helps all parties involved in the shipping process understand the specifics of the shipment.
Who is responsible for the goods during transit?
The carrier assumes responsibility for the goods once they are in their possession. The carrier must ensure the safe transport of the goods to the consignee. However, the shipper retains ownership rights until the consignee takes possession of the goods upon delivery. This structure helps clarify the responsibilities of each party during the shipping process.
Can a Straight Bill of Lading be transferred to another party?
No, a Straight Bill of Lading is non-negotiable. This means it cannot be transferred or endorsed to another party. The goods must be delivered only to the named consignee. If the shipper wishes to allow for transferability, they should consider using a Negotiable Bill of Lading instead.
What are the advantages of using a Straight Bill of Lading?
One key advantage is the clarity it provides in the shipping process. Since it is non-negotiable, it reduces the risk of disputes regarding ownership during transit. Additionally, it simplifies the delivery process, as the carrier knows exactly who is authorized to receive the goods. This can lead to a more efficient and secure transaction.
What happens if there is damage or loss of goods?
If goods are damaged or lost during transit, the consignee should file a claim with the carrier. The Straight Bill of Lading serves as proof of the contract and receipt of goods, which is crucial in such cases. The carrier may be held liable for damages unless they can prove that the loss was due to an exception outlined in the terms of the bill.
Is a Straight Bill of Lading legally binding?
Yes, a Straight Bill of Lading is a legally binding document. It establishes the terms of the shipping agreement between the shipper and the carrier. Both parties are obligated to adhere to the terms outlined in the document. Failure to comply can result in legal consequences.
How can I obtain a Straight Bill of Lading?
A Straight Bill of Lading can typically be obtained from the carrier or freight forwarder handling the shipment. It may be available in a physical format or as a digital document. Ensure that all relevant information is accurately filled out to avoid any issues during transit.
What should I do if there are errors on the Straight Bill of Lading?
If errors are found on the Straight Bill of Lading, it is important to address them immediately. Contact the carrier to request corrections. Any inaccuracies can lead to complications during shipping, including delays or disputes regarding the delivery of goods. Timely communication is essential to resolve these issues efficiently.